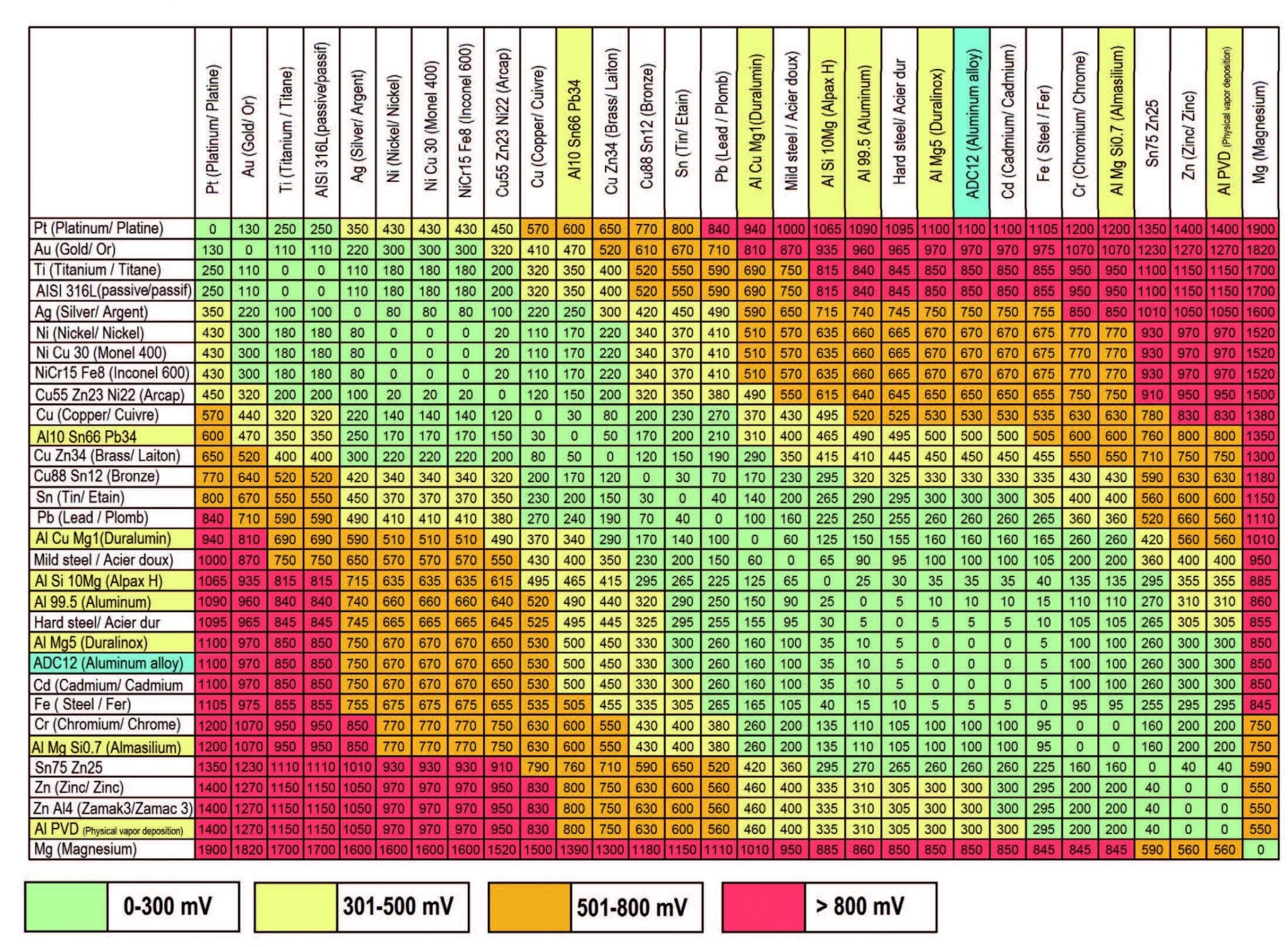
Dissimilar Metals Chart
Dissimilar Metals Chart - The greater the potential difference is, the greater the tendency for corrosion. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals with different potentials are placed in electrical contact in an electrolyte. When working with copper or aluminum use antioxidant pastes. Web we are aa metals, inc, one of north america’s largest master distributors of quality aluminum and stainless products. Web galvanic or dissimilar metal corrosion is electrochemical corrosion that occurs when one metal comes in contact with another material. Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte, separate them with a dielectric material such as insulation, paint or similar surface coating. Web this article examines how dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion. Web when design requires that dissimilar metals come in contact, galvanic compatibility can be managed by finishes and plating which protects the base materials from corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals with different potentials are placed in electrical contact in an electrolyte. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. We also provide other helpful methods for avoiding galvanic corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. • harsh environments, such as outdoors, high humidity, and salt environments. First there must be two electrochemically dissimilar metals present. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. A typical rule of thumb is that voltage differences of 0.2 volts or more suggest a galvanic corrosion risk. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). In this article, we'll look at an example to illustrate the use of the galvanic table. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. This conversion resource can help you determine what metal gauge you may need. Web this. Web galvanic corrosion potential is a measure of how dissimilar metals will corrode when placed against each other in an assembly. Web galvanic or dissimilar metal corrosion is electrochemical corrosion that occurs when one metal comes in contact with another material. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal. It includes a chart that shows how different plating materials react to one another with regard to their galvanic potential. Web this slide includes a chart of galvanic corrosion potential between common construction metals. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of acid. Web galvanic or dissimilar metal corrosion is electrochemical corrosion. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte, separate them with a dielectric material such as insulation, paint or similar surface coating. Web when two different metals are in contact and exposed to a common electrolyte, one of the metals experiences accelerated corrosion while the other is protected. When working with copper or aluminum use antioxidant. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. This type of accelerated corrosion between dissimilar metals is referred to as galvanic corrosion. • harsh environments, such as outdoors, high humidity, and salt environments. Web choosing the right size or area of the joined. The greater the potential difference is, the greater the tendency for corrosion. Web read on to find out about what it is and how to use it to analyse the compatibility of joining metals. Web chart sheet metal gauge. Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially. Web the susceptibility of different base metals to corrosion while in contact depends upon the difference between the contact potentials or the electromotive voltages of the metals involved. Web galvanic or dissimilar metal corrosion is electrochemical corrosion that occurs when one metal comes in contact with another material. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Web below,. Web when design requires that dissimilar metals come in contact, galvanic compatibility can be managed by finishes and plating which protects the base materials from corrosion. • harsh environments, such as outdoors, high humidity, and salt environments. When working with copper or aluminum use antioxidant pastes. Web choosing the right size or area of the joined metals: When dissimilar metals. The cart to the left is galvanic series in flowing sea water. • harsh environments, such as outdoors, high humidity, and salt environments. The greater the potential difference is, the greater the tendency for corrosion. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte, separate them with a dielectric material such as insulation, paint or similar surface. • harsh environments, such as outdoors, high humidity, and salt environments. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. The cart to the left is galvanic series in flowing sea water. The greater the potential difference is, the greater the tendency for corrosion. Web this slide includes a chart of galvanic corrosion potential between common construction metals. Web chart sheet metal gauge. Web the susceptibility of different base metals to corrosion while in contact depends upon the difference between the contact potentials or the electromotive voltages of the metals involved. Web this article examines how dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion potential is a measure of how dissimilar metals will corrode when placed against each other in an assembly. There are three conditions that must exist for galvanic corrosion to occur. You can also learn more about overcoming potentially compatibility issues between metals. Electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of acid. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Web but when you step onto a jobsite, working with dissimilar metals turns into a whole new monster with dire potential consequences. This conversion resource can help you determine what metal gauge you may need. In this article, we'll look at an example to illustrate the use of the galvanic table.Dissimilar joining of Al with steel? r/Welding
Dissimilar Welding Chart Stainless Steel Transition Metals
Galvanic Reaction Chart
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion with… American Galvanizers Association
Dissimilar Metals Corrosion Chart
Dissimilar metal corrosion with chemical filmed (Alodine, Iridite
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion Chart
Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals A Visual Reference of
Galvanic Corrosion Chart Dissimilar Metals
Design Calculations of Lightning Protection Systems Part Fifteen
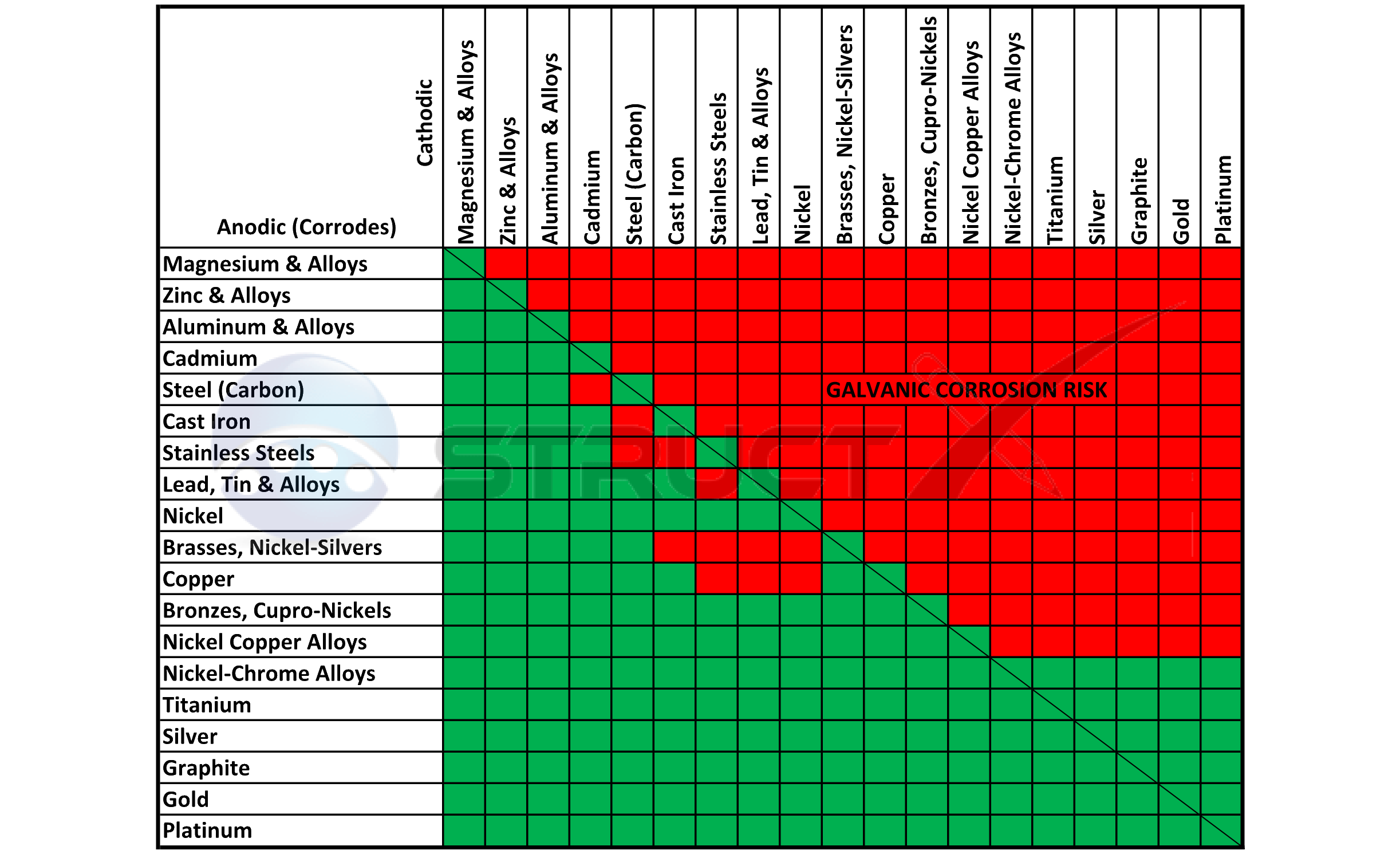
A Typical Rule Of Thumb Is That Voltage Differences Of 0.2 Volts Or More Suggest A Galvanic Corrosion Risk.
First There Must Be Two Electrochemically Dissimilar Metals Present.
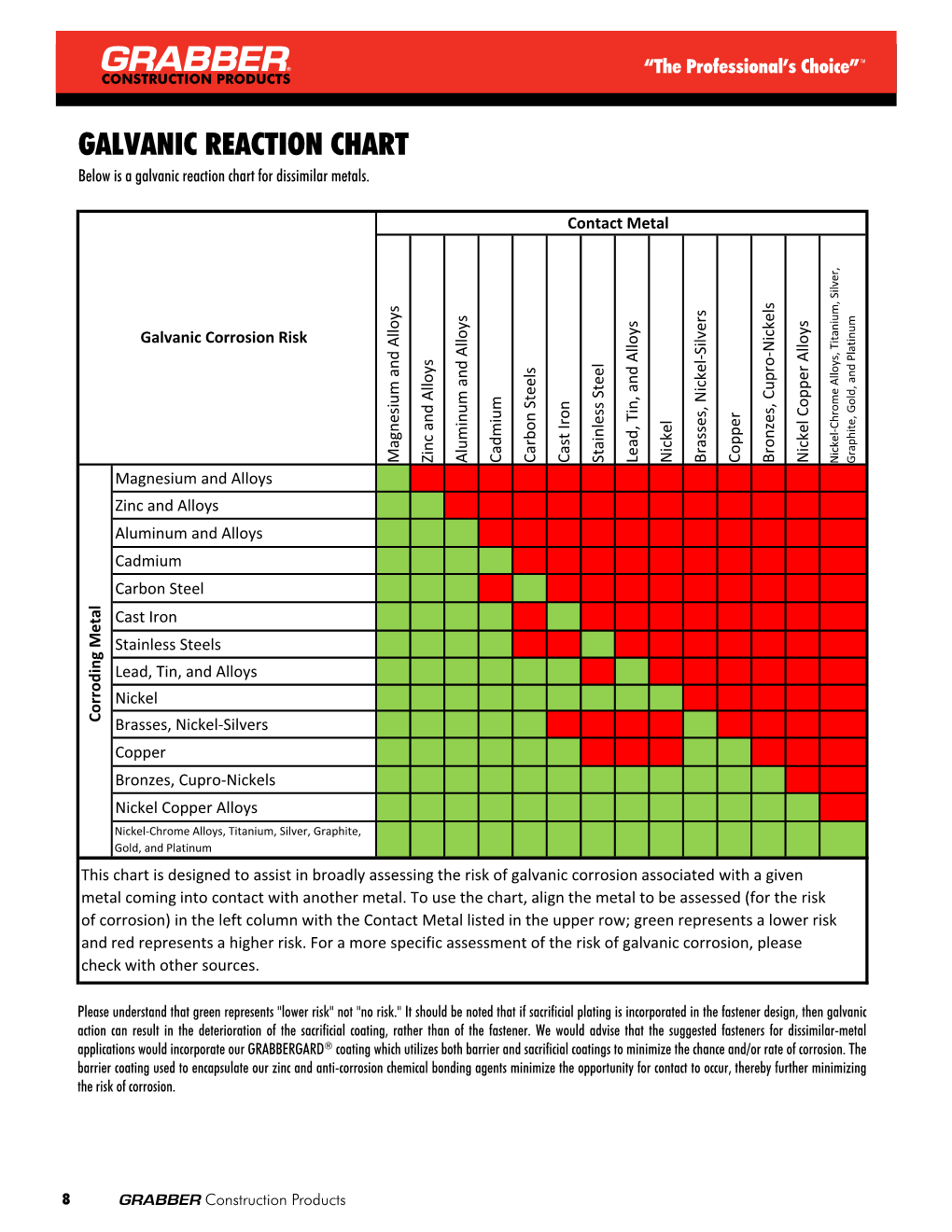
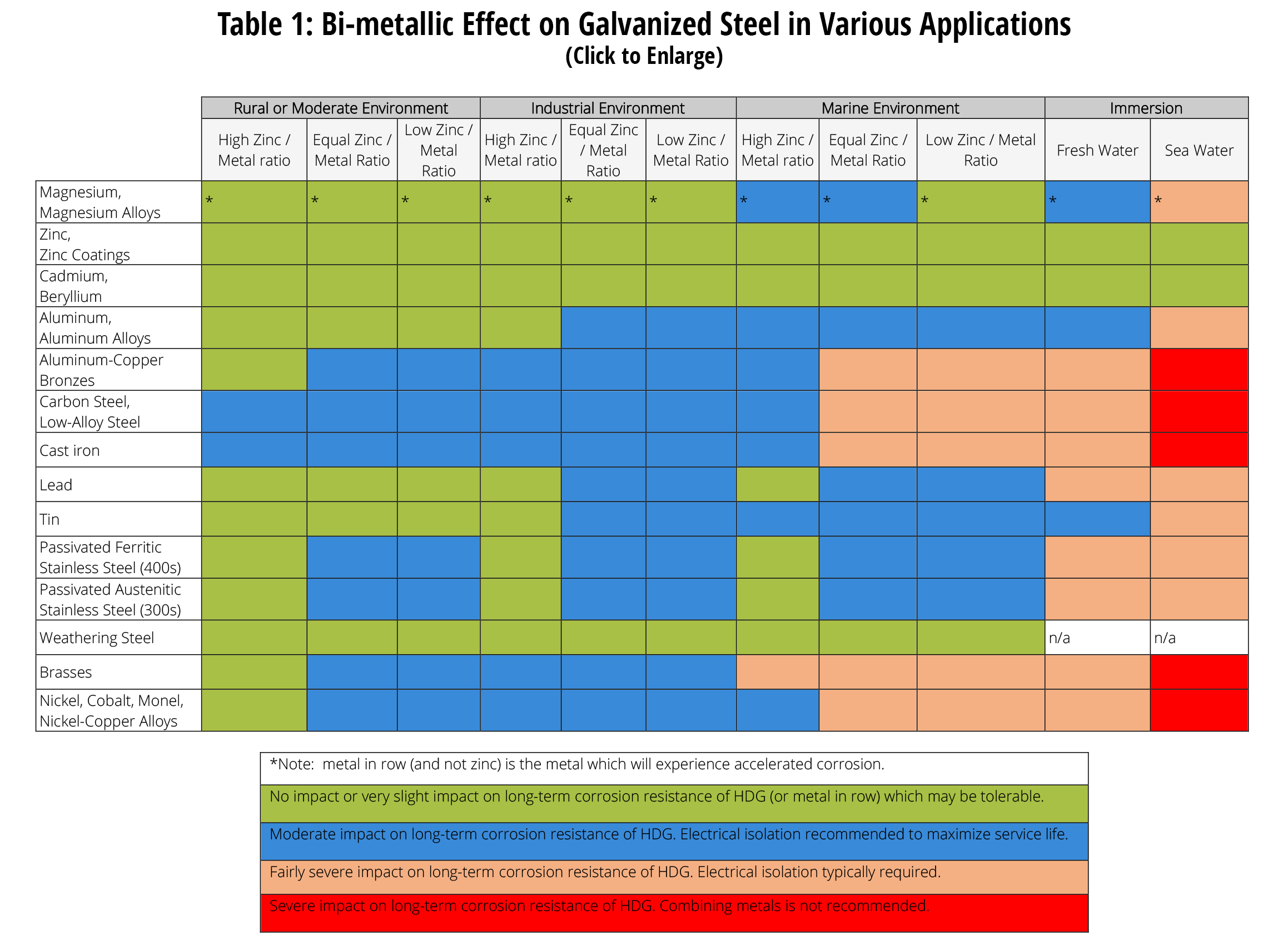
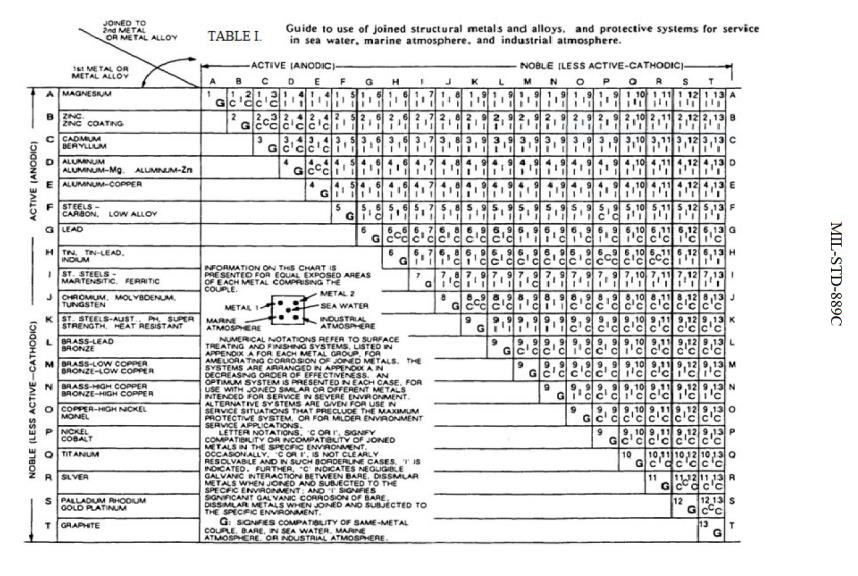
This Chart Is Designed To Assist In Broadly Assessing The Risk Of Galvanic Corrosion Associated With A Given Metal Coming Into Contact With Another Metal.
Web When Two Different Metals Are In Contact And Exposed To A Common Electrolyte, One Of The Metals Experiences Accelerated Corrosion While The Other Is Protected.
Related Post: